Discover more about S&P Global’s offerings
Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer LoginsContents
Cyber attacks through the lens of geopolitics
COVID-19, in addition to catalysing further digitalization — government e-services, remote work, digital currency and e-learning — has accelerated the extent to which we experience life online. People are now connected at an unprecedented scale and speed by digital technology, but this has allowed malicious online actors to behave more aggressively.
The same digital technology that allows people to connect enables cyber threat actors to share innovations, skills and tools. This leads to growing concern from governments and businesses as cyber attacks become more frequent and more complex.
At S&P Global, we recognize that cyber risks are part of the broader geopolitical risk outlook. This means that, much like terrorism, interstate war and other security risks, we must track cyber risks to understanding the broader geopolitical risk environment.
Cyber attacks should be understood as a tool, i.e., a means by which malicious online actors can effect change designed to achieve their desired political or financial ends. As a tool, cyber attacks offer a great deal of anonymity and deniability for the actors involved.
The political and social factors that determine when cyber attacks are employed must be carefully considered. Hybrid warfare is becoming normalized, and cyber threats to governments and companies are increasing.

Quantify the financial impact of cyber risk
Cyber attack incidents in recent years
Critical national infrastructure (CNI), such as the shipping industry and nuclear power plants, has been an especially attractive target for cyber threat actors in recent years. Cyber attacks targeting CNI are an effective way to maximize disruption and damage. A substantial and coordinated effort is required to protect these systems, both public and private, as they are essential to maintain state services and to ensure the business environment within a country operates smoothly.
Some states have invested in significant resources to detect and repel cyber attacks against CNI, but no country can fend off all cyber threats, and no technology is "unhackable."
Australia’s second-largest telecom company, Optus, said Sept. 22, 2022, that the personal data, including license or passport numbers, of nearly 10 million customers was leaked by hackers. Australian Cyber security Minister Clare O’Neil said the data breach was caused by vulnerabilities at Optus as the hack “was not particularly technologically challenging.” A ransom demand was reportedly made for US$1 million in cryptocurrency in exchange for the data, but Optus did not comment on whether the ransom demand was authentic.
Moldova’s Information Technology and Cyber Security Service said in January 2023 that a coordinated phishing attack on government bodies and institutions was attempted. Hackers reportedly targeted more than 1,300 email accounts associated with government services.
This highlights an ongoing battle against cyber risks for Moldova, which recorded a sharp increase in the number of attempted cyber attacks in 2022, possibly due to its support of Ukraine amid the Russia–Ukraine war. Experts warn of an elevated risk of cyber attacks against government and private sector IT networks in Moldova, including against media outlets, government websites and CNI such as power, water and gas distribution networks.
According to experts, hackers have also maintained a constant campaign of cyber attacks against Ukrainian, NATO, EU and other Western entities, principally targeting government and defense-related organizations. Cyber security analysts have suggested that hackers affiliated with Russian military intelligence are becoming more aggressive and more direct in their attacks.
The European Parliament website was inaccessible due to a cyber attack for several hours in late 2022, soon after legislators passed a resolution denouncing Russia as a "state sponsor of terrorism"; a pro-Kremlin group subsequently claimed responsibility for the cyber attack. Separately, the Microsoft Security Threat Intelligence Center has attributed cyber attacks against Ukrainian and Polish transport and security organizations to hackers backed by the GRU, Russia's military intelligence directorate.
<span/>Cyber attacks on the energy sector
In the third quarter of 2022, cyber attacks on energy and commodities infrastructure escalated sharply and reached a record high, according to the October 2022 update of S&P Global Commodity Insights’ “Energy Security Sentinel.”
Only two cyber attacks targeted the energy market in the second quarter of 2022. This increased to five incidents in the third quarter of the same year. These incidents were focused on the power, gas and nuclear sectors rather than oil.
Lithuania's state-owned energy group Ignitis, Ukraine's state nuclear power company Energoatom and Greece's largest natural gas supplier DESFA were among the companies hit by cyber security incidents over this period.
Cyber attacks have emerged as a growing threat to commodity supply chains. As a result, energy companies are prioritizing cyber security. Cyber systems for energy assets are on high alert due to a rise in cyber threats as the West tightens sanctions on Russia over its invasion of Ukraine.
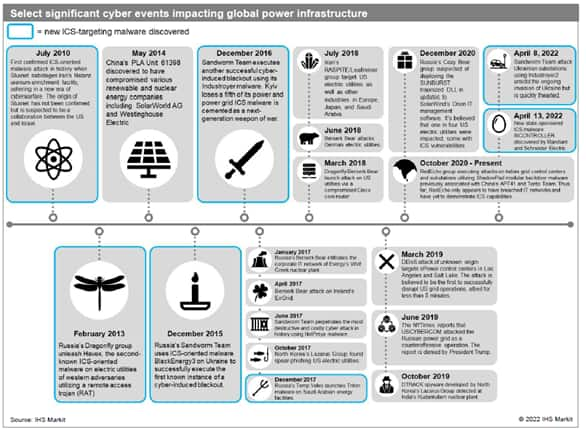

Significant cyber events impacting global power structure
Use of ransomware in energy industry cyber attacks
Ransomware cyber attacks have become an issue for the energy industry. Ransomware typically begins as a phishing attack, an exploitation of internet-exposed vulnerable software or an IT hygiene deficiency (a misconfiguration of an internet-exposed system).
The attacker takes control of the underlying system and can then move to other systems across the network. The malware broadly disables the network, allowing the attacker to hold the target for ransom until it pays, at which time the attacker usually sends a decryption key to unlock the target’s files.
The first major reported ransomware cyber attack within the energy industry was the 2017 WannaCry ransomware attack, with WannaCry being a ransomware variant developed by North Korea that spread widely from company to company to impact businesses across the globe.
In May 2021, the Colonial Pipeline ransomware cyber attack by the DarkSide group raised ransomware alerts across the sector. Colonial was not the first energy company to experience a ransomware attack in 2021. It was not even the only pipeline company to suffer one that month.
The most sensational and well-publicized results of the Colonial incident — the pipeline shutdown and the resulting gasoline shortages and gasoline hoarding — were the result of Colonial’s decision to shut certain systems down for safety, not the result of encryption of those systems.

Measure and manage your cyber risk profile
Investment in cyber security as a necessary part of the energy transition
Cyber security in global power systems is a necessary pillar of the energy transition, yet investment in this area has struggled to keep up apace with investment in next-generation power resources, smart grids and electrification. Since 2010, seven instances of unique malware cyber attacks have targeted the industrial control systems that reside on the operational technology networks, as opposed to IT networks, of the bulk electric system.
Meanwhile, vulnerabilities to cyber attacks stemming from internet of things devices have flourished throughout the power distribution segment. Cyber security represents a unique business expense for energy transition investors, one that cannot be categorized as a variable or fixed cost.
Cyber security requires continuous investment in an area where best practices are a moving target due to its evolutionary, adversarial and asymmetric nature.
Some of the key features of the energy transition exacerbate the need for cyber security investment in the power industry. For example, the electrification of new industries makes the grid an increasingly valuable target for adversarial nation states, or state actors looking to disrupt economies as well as non-state actors looking to extract a ransom.
<span/> In this sense, cyber security deserves attention as a key coefficient of the energy transition equation.
<span/>The bottom line
Political context is a critical factor when considering the likelihood of a country or company being targeted for significant cyber attacks. Nation-state actors who perform targeted intrusions to inflict damage, disrupt or steal valuable information at the behest of a government are usually the most capable and best-resourced cyber threat actors. Cyber criminals, cyber threat actors who perform malicious attacks for financial gain, may also operate within this context at the behest of nation-state actors.
We believe that approaching cyber attacks and digital threats from a geopolitical perspective permits a better understanding of the motivations, capabilities and exposure of both cyber threat actors and their targets.
<span/>Related cyber attacks research and analysis
Looking for cyber attacks solutions?

Cybersecurity package
The Cybersecurity Package is the ultimate one-stop source for technical knowledge, guidance and best practices on cybersecurity, pulling together the latest standards and reference works from the world’s most respected publishers and leading authorities.

Cyber risk solutions
Cyber Risk preparedness empowers companies to build comprehensive strategies with insight into the most pressing risk factors. Employ our Cyber Risk Assessment and Cyber M&A Assessment to support your cyber risk preparedness.

Alliance for telecommunications industry solutions (ATIS)
Standards from the ATIS dictate design, implementation and testing for information and communications technology. From cloud services to cyber security, these standards direct technology development and enable interoperability across the globe.
Cyber attacks FAQs
{}
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fen%2fenterprise%2fgeopolitical-risk%2fcyber-attacks%2f","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fen%2fenterprise%2fgeopolitical-risk%2fcyber-attacks%2f&text=Cyber+attacks%3a+What+the+hack+%7c+S%26P+Global","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fen%2fenterprise%2fgeopolitical-risk%2fcyber-attacks%2f","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=Cyber attacks: What the hack | S&P Global&body=http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fen%2fenterprise%2fgeopolitical-risk%2fcyber-attacks%2f","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Cyber+attacks%3a+What+the+hack+%7c+S%26P+Global http%3a%2f%2fwww.spglobal.com%2fen%2fenterprise%2fgeopolitical-risk%2fcyber-attacks%2f","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}


